The circular flow of economic activity is a very simple model of the entire economic process of a market economy. It represents the mutual exchange of financial and real flows between economic factors.
In other words, it shows the cyclical flow of money and products between households and businesses.
The overall economy consists of four main sectors. They are called economic factors. They are,
- Household Sector
- Business Sector
- Government Sector
- Foreign Sector
Each of these aspects is described below.
Household Sector
What is household in circular flow?
Households own factors of production, such as labour, land, buildings and capital. The business sector generates revenue by providing production factors.
Goods and services produced by the business sector are purchased by households. Household creates savings in an economy and they are pay taxes to the government. Also, they utilizes public services provided by the government.
Business sector
What is business sector in circular flow?
The business sector produces goods and services by purchasing production factors from the household sector. The business sector generates revenue from the sale of manufactured goods. They invest the profits of their businesses, and also give dividends to the owners and a portion of the tax to the government.
Government Sector
Government maintains national security, law and order and provides public goods, welfare goods and services to the public from tax revenue collected from the government.
In addition, the following are some of the services provided by the government.
- Protect the environment
- Provide services such as education and health
- Provide capital for economic common tasks such as highway and communication
- Provide consumer subsidies to households
- Provide production subsidies to the business sector
Foreign Sector
Foreign Sector includes the import and export of goods and services. This leads to the receipt of foreign factor income and payment.
The Circular Flow in a Two Sector Model – Simple Economy
Both the household and business sectors operate in a simple economy. In this economy, the household sector supplies all of its production factors to the manufacturing sector and utilities the proceeds completely. There is no government savings and no capital goods production in this economy.
The following diagram can be used to illustrate the interrelationships between economic factors in explaining the functioning of a simple economy in terms of circular income flows.
Circular flow of economic activity diagram
The circular Flow in a Two Sector Model – Simple Economy
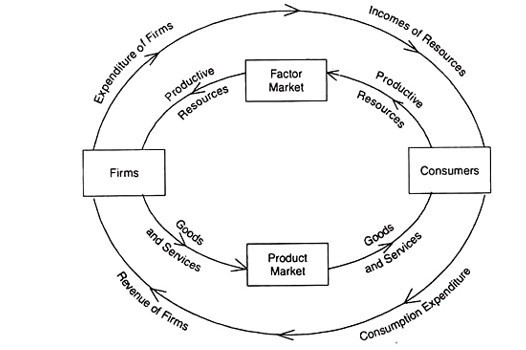
The above diagram identifies the three approaches to national accounting.
The business sector combines production factors derived from the household sector to produce goods and services. (land, labour, capital, etc). In relation to national accounting, it is called the product approach.
The business sector buys the production factors from the household sector. Then a factor income stream goes to the household sector. For example, wages for labourers, interest & profit for capital and rent for the land. This is the revenue approach in relation to national accounting.
The business sector supplies their goods & services in the goods or product market. The household sector buys the goods & services produced by the business sector. The household sector will bear the cost. It is called the expenditure approach in national accounting.
The Circular Flow in a Three Sector Model – Closed Economy
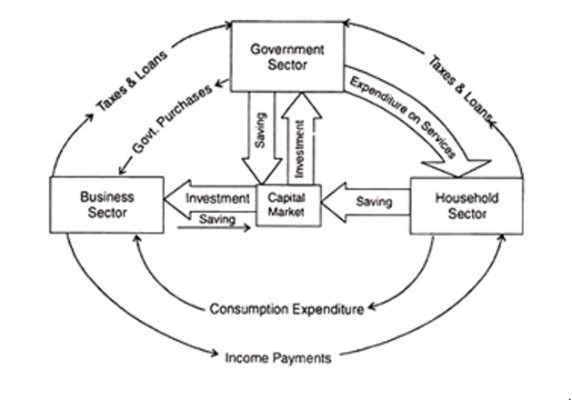
This model includes the household sector, producing sector and government sector. Here taxes and government purchases are added to the circular flow. Government purchases are inflow into a circular flow. Also, Taxes are an outflow from the circular flow.
Let’s firstly focus on the circular flow between the household sector and government sector.
Circular flow between the household sector and government sector
Here the household sector pays personal income tax, commodity tax etc. to the government sector. These are outflows (or leakages) from the circular flow.
But the government spends money on purchasing household services, providing pensions, providing unemployment benefits, providing food subsidies and providing public utilities such as education, health, water, and housing. These expenditures incurred by the government is an inflow into the circular flow.
In the diagram, we next focus on the circular flow between the business sector and the government sector.
Circular flow between the business sector and the government sector
Here the business sector pays all the types of taxes to the government. It is a leak (outflow) from the circular flow.
Also, the government sector purchases all its commodity needs from the business sector. In addition, the government provides subsidies and loans to companies. These are considered government expenditures. It is an inflow into the circular flow.
Next, let us consider how the trinity of households, businesses and the government sector behave in the circular flow.
Circular flow between households, businesses and the government sector
As shown in the figure, taxes flow from the household and business sectors to the government. There the government purchases goods from companies and factors of production from households.
The taxes levied by the government on the household sector will lead to a reduction in consumption and savings in the household sector. On the other hand, taxes levied on the business sector reduce investment and production.
In order to balance these situations, purchase from the business sector and the buying services of the household sector should be equated with the amount of the tax. Then in a circular flow the outflow and inflow are equal.
Also in some cases, if the net tax revenue is higher than the government expenditure, the government reduces the public debt and funds the capital market.
The Circular Flow in a four sector Model – Opened Economy
Four sector model is created by adding the household sector, business sector, government sector and foreign sector. The foreign sector plays a major role in the open economy. It describes how imports and exports behave in a circular flow. Let us describe them as follows according to the diagram.
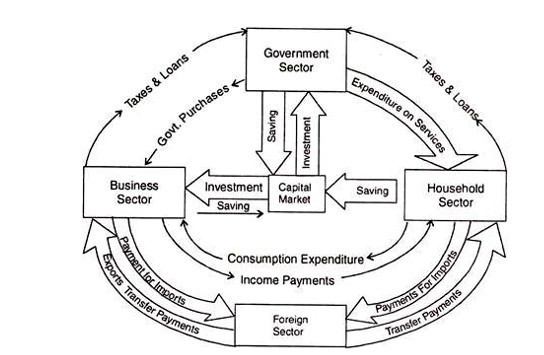
Export is the inflow of money into a circular flow. Import is a leak out of the circular flow. As shown in the diagram, the household sector purchases imported goods. Also in terms of business sector and foreign sector, the business sector exports goods to foreign countries. It is a cash flow to the circular flow.
Businesses also provide banking, overseas shipping and insurance services. Also, interest, dividends and profits to investments made with foreign countries. All of these flow into a circular flow. On the other hand, it is a cash flow.
Next, let us consider the leakage of circular cash flow from the business sector to the foreign sector.
The business sector imports capital goods, machinery, raw materials and consumer goods and pays for services received from foreign countries. These are leaks that occur in circular cash flows.
The government also imports and exports goods. Examples of imported goods are essential food items, foreign labour, car spare parts and capital goods. The government also borrows from the foreign sector. It also receives various subsidies from the foreign sector and foreign direct investment. The government has to pay for export of these goods to foreign countries.
And, also the government exports local goods, spices and local food beverages to foreign countries. There the government receives payments from foreign countries.
Importance of the circular flow of economic activity
- Used to analyse approaches such as revenue, expenditure and output in national accounting.
- To simply describe the whole economic process.
- Representation of reciprocal financial and real flows between economic factors.
- Used to estimate GDP.


