Learning Outcomes:
- Analyzes production factors used to produce goods and services.
- Specifies the characteristics of the production factors separately.
- Defines the productivity of product resources.
- Describes the factors that determine the productivity of product resources.
Production Factors
Production factors are used to produce the goods and services needed to satisfy human needs. Land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship are the factors of production.

These production factors can be further subdivided into two parts.
- Property Resources
- Human resources
Characteristics of production factors
1. Characteristics of Production Factors [Land]
All the gifts of nature used to produce goods and services belong to the land. Here the land is not just the earth but all the gifts of nature that can be used for the production process.
Example:
- geographical location
- weather
- Management Soil
- Streams
- Mineral resources
- Wild animals
- Marine fisheries resources
As mentioned above, land includes the surface of the earth as well as the interior of the earth.
Characteristics of the Land
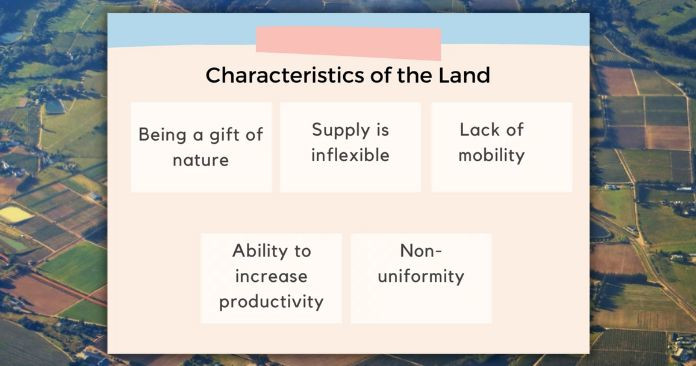
- Non-uniformity That is, the land takes different forms (location, climate, water resources, mineral resources).
The rent paid for the use of the land is rent.
2. Characteristics of production factors [Labor]
Labor as a factor of production means all the mental and physical effort that can be applied to the production process.
Characteristics of labor
- Labor is inseparable from the worker (it is inherent in man)
- The existence of an interrelationship between labor and time. (Labor is measured in terms of time, and labor is lost as time goes on.)
- The labor productivity of each worker is different (education varies depending on health)
- The ability of the worker to determine the value of the labor factor
What are the factors that determine the amount of labor resources?
- Population size (this mainly depends on birth rate, death rate, and net migration).
- Health condition
- Education and Skills
- Physical strength
Division of labor and specialization
The division of labor is the process of having different people at different stages of the production process.
Specialization is the ability of an individual, region, or country to engage in a single productive activity.
How the division of labor can be influenced to reduce production costs and increase competition
- As a worker specializes in one task over time, he or she acquires the ability to perform that task more efficiently.
- The special antecedent enables the introduction of unique production equipment and tools that enhance the productivity of the production process.
- The division of labor encourages innovation.
- Worker time is not wasted as there is no need to switch between different roles in the production process.
- Identifies the skills of the worker and allows the manufacturer to attach workers to the corresponding tasks and thereby increase efficiency.
- It is a great convenience for the organization to set up and implement worker training programs.
How can specialization cause product inefficiencies?
- Impairment of the entire production in the absence of the participation of a single worker.
- The narrow specialization of the worker.
- Risk of worker occupation due to narrow specialization.
- Social and relationship breakdown.
- International tough retention
3. Characteristics of production factors [Capital]
Capital is man-made, and manufacturing aids which help in production. This is a real asset. This is a wholesale concept, hence the name capital, mass.
Characteristics of capital
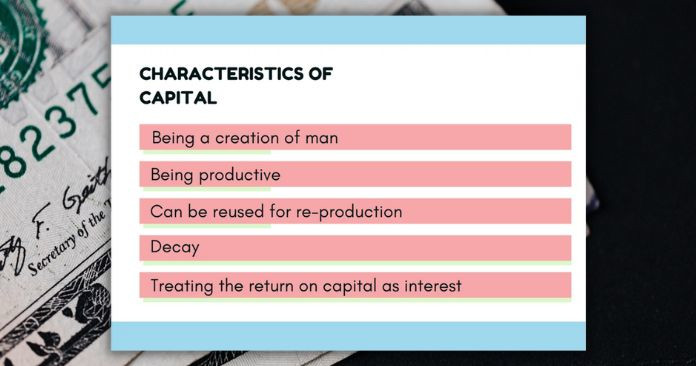
The nature of capital is determined by the level of technology present in a country.
Forms of capital
1. Physical capital / real capital / fixed capital
- Fixed capital includes durable capital assets that can be used continuously for the manufacturing process, such as factories and machinery stores.
- Fixed capital provides a certain amount of return to the asset holder throughout the period of use.
2. Working Capital / Circulating Capital / Stock / Screening
- The raw material used for the manufacturing process, the semi-finished product, the goods being manufactured, and the finished goods ready to be distributed is called circulating capital.
- These are important to keep the production process going smoothly and to prepare future production plans for a country.
3. Economic general working capital
- Capital goods that facilitate the production and distribution process of goods and services in an economy are called economic general working capital and are also known as economic infrastructure.
Examples: – Ports, airports, power systems, irrigation, water supply systems, and highways.
- Economic infrastructure encourages local and foreign private investment, which is currently provided by the government in many countries.
4. Social public working capital
- Capital goods that provide services that are used to meet basic human needs are called social working capital.
- School buildings in the field of education, hospital buildings in the field of health, operating theaters, medical laboratories, and equipment, as well as waste disposal pipelines and drinking water supply systems, are covered under this and social welfare is achieved through this.
5. Human capital
- Advanced labor is called human capital. There are several ways in which labor can be improved.
E.g. education, training, research, experience, and health status
- Human capital can increase worker productivity and increase the quantity and quality of production.
- Examples of enhanced labor-intensive human capital include designers, university lecturers, trainee teachers, and specialist physicians.
- Capital in a country comes from investment. The investment comes from savings. Therefore, there is an interrelated link between capital, investment, and savings.
- The savings of an economy can be categorized into domestic and foreign savings, domestic savings, business savings, and government savings.
- Household savings are a portion of household income that is not consumed on a daily basis.
- Part of the business profit is retained in the business as undivided profits. It is a business saving. They are used for future investment.
- When savings are deducted from total government revenue, the balance is called government savings.
6. Natural capital
- The natural resources that exist in an economy are called natural capital.
Examples of natural resources are land, rivers, streams, and minerals.
- The proliferation of natural capital is important for economic growth.
7. Social capital
- Social capital is the institutional, normative, values, association membership, and network of relationships that develop the quality and quantity of social interaction.
The Importance of Social Capital :
- Contributing to the well-being of society.
- Increasing community productivity.
- Develop social strength and confidence.
- Contributing to sustainable development.
- Minimize ethnic conflicts.
- Reducing poverty.
- Government efficiency.
Is money considered capital In economics?
Capital is the real assets used to support the production process. Although money can be used to acquire the real assets needed for the production process, money cannot be used as a real asset in the manufacturing process, so in economics, money is not subject to capital.
Why does capital differ from land and labor?
Land and labor are the primary means of production and capital is the secondary resource. Labor is the biological origin and land is the product of nature.
4. Characteristics of production factors [Entrepreneurship]
Entrepreneurship is the process of organizing, directing, and taking risky policy decisions by assembling the factors of production scattered throughout an economy.
This occupies a more important place among the factors of production.
As innovation takes place through entrepreneurship, it has a powerful impact on the growth of capital.
The role of an entrepreneur in an economy
1. Organizing production activities
Initial efforts are made to combine new product resources to produce a new product or service.
2. Making basic business policy decisions
The entrepreneur also has to make the basic decisions of a business. These are policy decisions, not day-to-day business decisions. The success of a business largely depends on those, that is, product decisions.
3. Introducing innovations on a commercial basis
The entrepreneur is the one who successfully introduces innovations on a business basis. Innovation is about creating something new that meets customer needs or reduces production costs.
4. Risk
The entrepreneur is also a risk-taker, that is, he has no guarantee that it will be successful in introducing new products to the market, so he devotes resources to his business at great risk.
Characteristics of entrepreneurship
- Being a human factor
- Initial energy
- Ability to face challenges successfully
- Leadership qualities
- Future Vision
- Self-confidence
Question
Identify the production factor that includes the following:
- Petroleum deposit – Land
- Farm – Capital
- Climate – Terrain
- Red laterite soil used for tea cultivation – Land
- Medical Clinic – Labor
- Ocean Fish – Land
- Natural harbor – Land
- Wildlife – Land
All right then. I really hope you enjoyed this article. Have you a question about something that I covered.
Either way, I’d like to hear from you. So go ahead and leave a comment below.