What are the 4 Phases of Business Cycle? Let’s Discuss.
There are four main stages in a business cycle. A business cycle refers to the cyclical behavior of real gross domestic product over time. A business cycle can identify fluctuations in the macroeconomy. That is, the business cycle represents short- and long-term fluctuations in macroeconomics.
There are four main stages in a business cycle.
- Recession
- Trough
- Expansion
- Peak
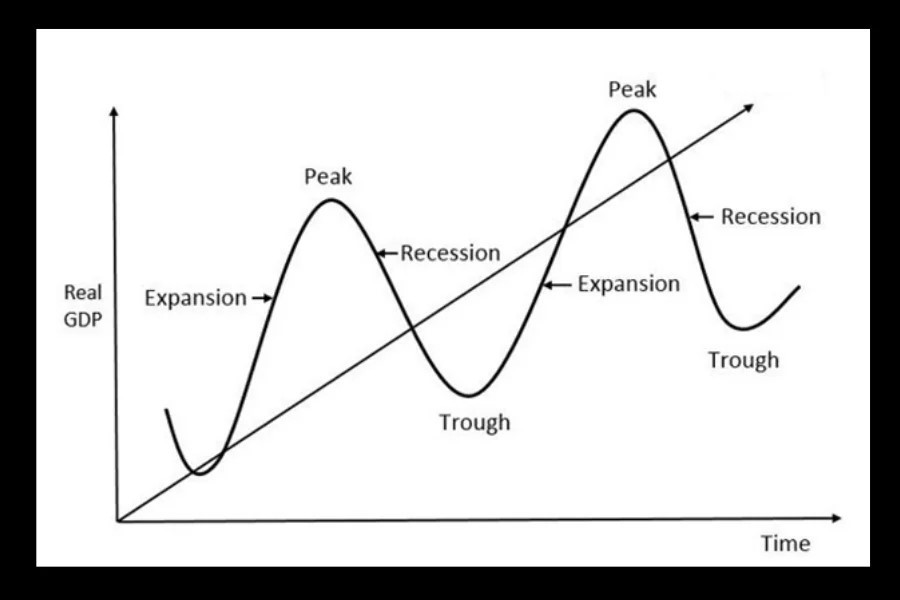
4 Phases of Business Cycle: Recession
A recession means a weakening of the overall economic process. There, real GDP will fall. Employment is also falling. Such a setback can last up to six months in a row. If this recession lasts more than 6 months, it becomes a depression. This is due to the continuous breakdown of real production and employment for more than a year.
There may be a temporary downturn in the economy. It is not the same as going backward in a business cycle. A temporary setback is caused by adverse weather conditions. This can ruin the harvest. But this is a temporary setback. These temporary setbacks may occur in some months. This is not the same as the downturn in a business cycle.
Because of this, one has to wait a considerable amount of time to identify the recession phase and the temporary downturn of a business cycle. After a recession of at least six months, it is called a recession.
Characteristics of Recession
- Located between top and bottom
- Decreasing employment
- Decreasing real production
- Deflation situation arises
- GDP declines
4 Phases of Business Cycle: Trough
The trough phase means when the economy slows down and begins to expand again. It shows a relatively low level of overall economic activity. Here the employment, productivity, and national income of the overall economy have all declined and reached a maximum. No more recession
Characteristics of Trough
- It is the peak of the recession.
- Employment, real production, deflation, GDP are at the lowest level. Will not decline further.
4 Phases of Business Cycle: Expansion
The expansionary phase is the period in which the economic process continues to grow from the bottom up and move upwards. The peak can be considered as the peak of the expansion phase. During the expansion period, employment, output, national income, and common price level grow continuously.
Characteristics of Expansion
- Located between the bottom and the top
- Employment rises.
- Real production increases.
- Inflation will occur
- National output rises.
4 Phases of Business Cycle: Peak
The peak of the expansion phase is called the peak. Here employment, national income, and general price level have all grown to the highest level. No further growth.
Characteristics of Peak
- It is the peak of the expansion phase.
- Employment, real production, deflation, GDP are at a high value. No further growth.
In a business cycle,
- The period between top and bottom shows the recession.
- The expansion phase takes a long time to occur.
- The recession phase takes a short time to occur.
- The distance between two peaks is called the distance.
- The gap between the potential output and the actual output is called the output gap.
- The output gap is divided into a positive output gap and a negative output gap.
- When the actual output is higher than the potential output, it is called the positive output gap. When the actual output is lower than the potential output, it is called a negative output gap.
What stage is appropriate for the economy?
Is it Expansion phase?
No. During this period, the volume of goods, employment, and national income will increase, but at this stage, the actual output will be higher than the potential output.
What is Potential output
Potential output is the maximum quantity of goods that can be produced using all the resources available to the economy. The potential output level indicates the production capability curve. The actual output is the quantity of goods currently being produced. The potential output indicates the long duration and the actual output indicates the short duration
There are no uncultivated lands in the economy at the time of potential completion. There are no unemployed people. Potential output is the maximum quantity of goods an economy can produce. So how can the actual output be higher than the potential output? What happens here is that a worker works some extra time in addition to his working hours. Also, more land use than is required. That is overuse. Also, commodity prices continue to rise during the expansion period. That is, there will be inflation. This is not so good for the economy in the long run. Therefore, the expansion phase is not the most suitable phase for the economy.
Is it Recession phase?
What happens here is that the actual output is lower than the potential output. That is to say, the quantity of goods that an economy actually produces is less than the quantity of goods that an economy can produce.
This means underutilization. What is happening here is that lands that can be used for cultivation are not being used for cultivation. If a worker can work 8 hours a day, he is working five hours. Commodity prices fall during the downturn. That is, there is attention. This discourages the producer and reduces production. If so, the recession is not good for the economy either.
Which stage is best for the economy?
The economy is best suited for a time when the expansion phase is reversing and potential output and real output intersect. It means actually producing the maximum amount of goods that an economy can produce.
Resource allocation efficiency is shown when the potential output level and the actual output level coincide. (Resource utilization) Because of this, every economy is working to reduce the positive output gap and the negative output gap.
The policies used for this are called macroeconomics policies.
- Fiscal policy
- Monetary policy